What Is Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis) Treatment?
Atopic dermatitis is a common, often persistent skin disease that affects a sizable percentage of the world's population. Atopy is a specific type of allergic sensitization associated with asthma, hay fever, and chronic dermatitis. The disease has a known hereditary component and is more common in families affected by these diseases.
In atopic dermatitis, the skin is extremely itchy and often inflamed. It causes redness, swelling, vesicle formation (bubble), cracking and crusting. Dry skin is also common in most patients with atopic dermatitis.
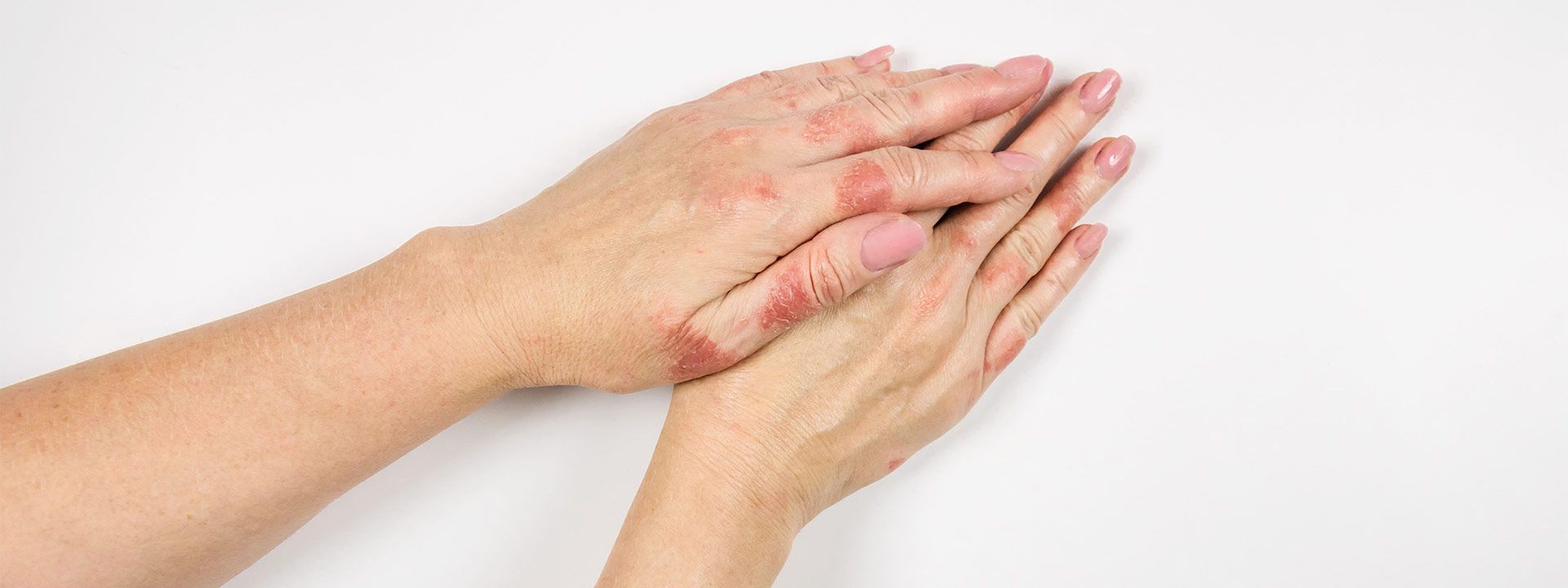
Egzama (Atopik Dermatit) Tedavisi
Atopic dermatitis is very likely to be chronic. In such cases, various treatments that take months or years need to be tried. Even if treatments are successful, the disease can recur. As in any disease, early diagnosis and treatment are important in this disease. Regular skin hydration and avoiding substances that cause dryness of the skin can be helpful for treatment.
Apart from this, creams that control itching and help repair the skin are recommended by the doctor. These creams contain corticosteroids and it is important to use them in doses. In cases of overdose, it causes extreme thinning of the skin and causes other reactions.
Some creams containing calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are also recommended to strengthen the immune system. It is suitable for use in all individuals older than 2 years to prevent and control skin reactions. After using such creams, it is necessary to protect from the sun. In addition, if any infection has occurred on the skin, antibiotic treatment is also required. Short-term use of antibiotics may be necessary to treat this infection.
